Top profit margin on schemes for fmcg retailers how to calculate?
Distributor margin, profit and retail price in FMCG and other industries

Not all distribution margin is profit
A manufacturer or supplier, needs to sell products to consumers, have to work with distributors and retailers, both in home country and abroad. The margin for a distributor may range from 3% to 30% of the sales price, the margin for the retailer may range from very little to 60%. This all depends on the type of product and who pays for the marketing activities.
Not all FMCG distribution is profit
You know the cost price for your goods, and you should have an idea of the sales price for the consumer, excluding any taxes. Anything in between is margin that you will have to share with your distributors, retailers or value added resellers.
However, not all margin is profit. In order to earn the margin, distributors and retailers have to make costs, for example for shipping, storage, financing and of course selling the goods. They also have their overhead, leaving only part of the margin as their profit. When negotiating with the parties further in the distribution chain, you will have to take this into account.
Average retail margin and distribution margin
| Product category | Distributor | Retailer |
| Fast moving consumer goods | 3-10% | 8-40% |
| Clothing and apparel | 15-30% | 20-50% |
| Electronics like mobile phones | 3-7% | 3-7% |
| Cars | 5-15% | |
| Furniture | 30-50% | |
| Jewelry | 30-60% | |
| Electrical equipment and lights | 5-7% | 15-25% |
Please note that these figures are indications and especially for distributors heavily depend on the tasks that a distributor should do. For fast moving consumer goods 3 to 10% may be fine for just the physical distribution, but if the distributor also does promotional efforts, this percentage should be much higher. Therefore we have to look into detail in the various roles of the parties in the distribution chain.
What is the role of the retailer in distribution?

A retailer sells goods to the public in relatively small quantities for usage or consumption rather than for resale. A retailer can for example be a supermarket, preferably with multiple outlets. The retailer is the last shackle in the distribution chain and has the best information on what sales price is still acceptable.
The actions of most retailers are aimed at maximising the margin on their assets. And their most important asset is shelf space. So they will multiply the volume of your product with their margin to see how much they can earn and compare it with other products that they could have on the shelve.
What is the role of the distributor?
The distributor is the middle men between the manufacturer and the retailer, or between the manufacturer and businesses that integrate the product or use it for their own consumption. There can be a chain of distributors, for example a global distributor who sells to specialised distributors for certain industries. In B2B markets, e.g. for desks, complicated machinery or cleaning services, you generally have no retailers.

The main assets of a distributor are his sales force, transportation means and storage. He will try to optimise the margin he can get with these assets. So it helps if you create an easy ordering process for him, with packaging that he can easily split and handle, and good documentation for his sales force.
Distributor price and retail price
Your distributors and retailers should be able to cover their costs and make a small margin.
Therefore the next step is to list their activities and add a value to it. These activities could include:
Transportation
Packaging and unpackaging
Storage
Financing
Marketing
Sales, either in personal sales or by putting the product in their shops
Adding up the estimated costs of these activities will give you a good basis for negotiations. Discussing the list will also help to clarify expectations, which is especially important if you work with foreign distributors.
Available retail and distributor margin calculation
How to calculate the distributor margin or retailer margin?
What is the profit margin for a retail store?
According to Vend’s Benchmarks Report the brand studied more than 13,000 retailers, the average gross profit margin in retail is 53.33% worldwide.
How much profit does a retailer make?
Since retail stores cater to a wide range of consumers, profit margins vary.
There is no ideal percentage, but values typically range from 5% to 7.5%.
How is FMCG margin calculated?
This is the cost price. The retailer adds Rs 2 as his value and sells the soap to the final consumer at Rs 10.
The margin of Rs 2 between the cost price and MRP is the mark-up. In this case, the mark up on the cost price is (2/8= 25%) and on the MRP is 2/10 = 20%.
The first step is to calculate what margin is available and which part of it should go to your distributors.
- The process begins with determining the cost of your goods. Be clear about which units you sell your products in, and be consistent in you calculations to take that as a basis.
- The next step involves establishing a MSRP (Manufacturer suggested retail price).
- Configure MSRP by considering the profit earned across all your sales channels and the product competition in the market. Also take into account applicable taxes, like VAT.
- Distributors and retailers typically get discounts on the MSRP in exchange for selling your products on behalf of you.
- Distributors usually command large discounts due to the bulk of their orders, and the number of retailers ordering from them.
- They don’t usually need too much support, except for notifications of new promotions and progress of the prices on your products.
- Anticipate hidden costs. Damages or product losses could occur during shipments.
- To avoid this, ensure quality containers which would require additional costs.
- Include it in your calculation of unit sales to adjust your margins.
- Most distributors and retailers would also ask for as many samples of your products as possible.
- Reasonable margins for your distributors should be computed only when all costs (including hidden variables and miscellaneous) are known.
The second step is to divide the margins along the distribution chain, e.g. between you, the distributor and the retailer.
Keep in mind the work that each party has to do and the risks they take. In general the profitability of a product is lower for the distributor than for the retailer but distributors have more sales due to the sheer volumes that they deal with.
Try to determine with what transfer prices it still is interesting for your distributor and when applicable your retailer to sell your products.
What is gross margin and net margin in FMCG Retail?

Trade Schemes are usually additional support in terms of Sales Promotion or Trade Promotion or Temporary Price Reduction extended to the trade considering quite a many factors like Competitor’s Activities, Seasonality, Company’s own agenda etc. etc.
Trade Schemes are of 2 types:
Primary Scheme & Secondary Scheme (Not to be confused with the Primary Sale & Secondary Sale mentioned above). You can read more about them here
2 methods by which pricing of products is done within a company: Mark-Up or Mark-Down and on that basis, the schemes, margins etc. are arrived at for its trade. The only difference between the 2 is the reference which they use; Mark-Up would use cost price as the reference and Mark-Down would use Selling Price as the reference.
1 case to 2 cases – Additional Discount of 9%;
3 Cases and above – Additional Discount of 10%
How Retailers benefit fromVendors/Company Salesmen?
It varies by retailer around the world. Vendors don’t normally handover a lump sum amount per product for the retailer to give them shelf space, though some retailers (few) still have a listing fee i.e. a basic fee for taking the vendors product. This is further supplemented by margin.
Margin : is the difference between what the retailer sells the product for to the consumer/shopper (for e.g.$2.00) and what it buys the product for from the Vendor ( for e.g. $1.50).
Margin in this case is $2.00 less $1.50 = $0.50 and can be expressed as a percentage by dividing $0.5 by $2.00 to be 25%.

There are many factors for a stable FMCG portfolio of products. I will list 2 key factors, distribution, and personal preference.
Distribution is often overlooked because sale happens because of availability. Deeper the availability, better the stability of sales in FMCG products. Very rarely there are replacement products for shampoos, toothpaste, beverages….Hence the shock of vanishing sales in the short term is very remote. Despite Amazon and Flipkart’s push, the digital market is just ~ 2% of the total market, 98% is physical outlet sales. In a country like India national distribution takes decades and the market is in the hands of dozen or so FMCG companies, not much considering the global markets.
FMCG buyers are very loyal to brands since its a personal preference. Changing or tweaking drastically will invite the wrath of brand switches and total abandonment. Product maturity in fact ensures better margins and tighter supplies. May not get rocket sales Y-o-Y but a good spike in the economy will ensure much better margins.
Does it mean the future will be the same? No way! Disruption is coming!

Personal preferences could change for better social values. Availability could be more local than centralized or hub & spoke distributions.
Difference between the wholesale and retail prices,margin and markup
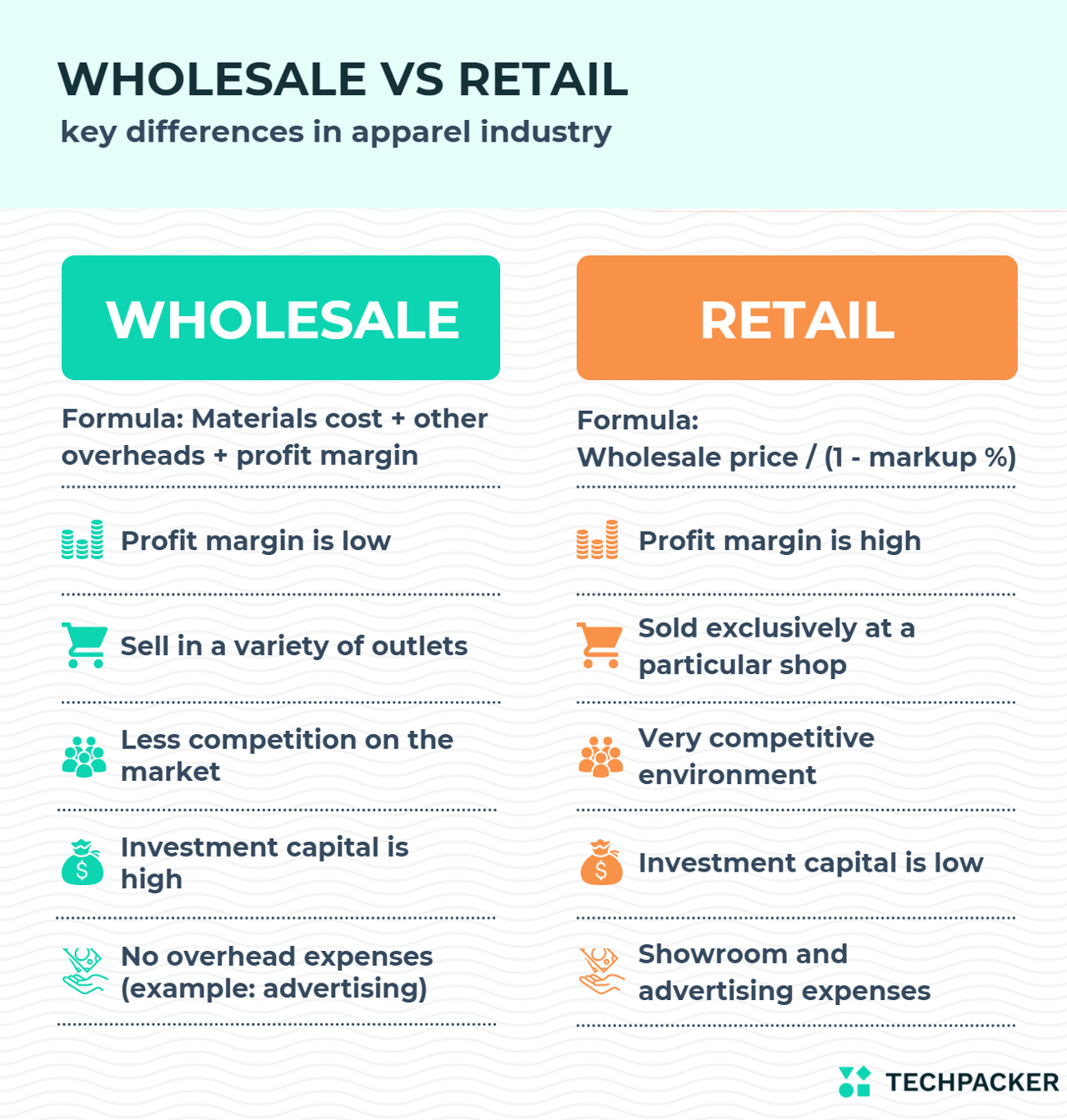
Many apparel business owners calculate the Wholesale Price by multiplying the cost of goods by two. In the apparel industry, business owners usually aim for 30-50% wholesale profit margin. The profit margin is what you earn when your product is sold. A profit margin is sometimes also called markup percentage.
Wholesale Price includes the materials costs, manufacturing and labor invested, other overheads like rent, electricity, etc., and a minimal profit margin.
Wholesale Price Formula:
Wholesal Price = Materials Cost + (Labour Invested x How Much You Value Time) + Other Overheads (Rent, Fixed Costs, Electricity, etc) + Profit Margin
calculate the Retail price of your garment add profit margin to your Wholesale price. In the apparel industry the retailers usually aim for 55-65% profit margin.
Retail Price Formula:
Retail Price = Wholesale Price / (1 – Markup Percentage)
The Retail price of the product can be suggested by the brand or the apparel manufacturer to the retailer. This pricing strategy is called Suggested Retail Price (SRP).
The key differences between Wholesale and Retail are:
- Wholesalers typically only deal with limited products, where retailers tend to handle many different products at one time.
- Retail profit margin (markup) is always higher than the Wholesale profit margin.
To do that ROI, you will need to realistically know the Returns(margins) he makes , the Investment he has and the number of times he turns over.
Now, wholesaling is an opportunistic business by nature, where selling prices can vary depending on quantity. Often the Wholesaler gives up margins for quicker, faster turnovers. I have know wholesalers who even buy and sell at the same price, and all the money they make are on selling the master cartons.. Investment is also difficult to estimate, as he procures credit, and often rotates many times before the bills are due.
We think it is a great time to be pursuing a career in marketing analytics as the world is now able to generate and store large amounts of data. However, analytical ability of processing that data is still to catch up. Having said that we can share the two most important factors one must have a good understanding of when analysing marketing data.
- How does the data link to the 3 Golden Metrics of any business : Value Sales, Profit and Market Share. One should be able to identify in a linear manner how anything being analysed links back to these 3 golden metrics
- Have the ability to understand and identify the difference between Causation and Correlation. For e.g. you might find that beer sales have a positive correlation with ice cream sales however beer sales do not cause ice cream sales. We know that warmer temperatures are causative and influence beer and ice cream sales.

How do you calculate the FMCG outlet base on the basis of a particular town population?
A rule of 150 Outlets Per Lac of Population is good coverage target that that one could go after.
Outlets beyond this 150 could be marginal; difficult and expensive to cover.
There are two types of retailer schemes which run in market –
Percentage Discount Basis – In this case when a salesman is going to take the orders in market, he will tell the retailer that you will 5% discount on buying 12 packets of a certain brand. if the Mrp is 10 rs of one pack , retailer margin is 10% mark up, then the 5% discount will be offer on the rate (PTR) at which retailer will buy it. The PTr for 12 packs in this case will be rs 109, so 5% discount will be given on PTR. These are mark up schemes.
- Quantity purchase scheme – Buy X, get Y free. In this case when a sales man is going to market, he will tell retailer that for e.g. if you buy 12 packs, then you will get 1 pack free. The scheme calculation will be 1/(12+1) it will give mark down calculation. Mark up calculation will be 9/109 (PTR). So the scheme communication can be done both ways. For accounting purpose its taken as mark down.
If you need to understand how schemes are calculated in FMCG, you need to understand markup and markdown margin.
Simple example
If you buy a pen for Rs 8/- and sell for Rs 10/- you earn Rs2/-
That Rs 2/- is your profit / margin and u want to know what % profit you make..
If you divide Rs2/- on buying cost Rs 8/- you earned 25% margin. This is called markup calculation.
If you divide Rs2/- on selling cost Rs 10/- you earned 20% margin. This is called markdown calculation.
Though the absolute profit amount is Rs 2/- you have two ways to arrive at profit percentage.

Work downwards from MRP, 12% retailer, 8% stockist/distributor, 3% C&FA, 2% transportation, 2% salary of sales force, 10% marketing expenses the combination needs to be tweked as per business and products projection and demand.
ROI =((Gross income- Expenses)/net investment)*12
Gross Income = margin on invoice + support \incentive earned from company.
Expenses= warehouse rentals+ manpower dedicated + vehicle running cost+ others
investment= (stocks from company + credit in market + investment in offices assets + vehicle down payment) -co credit.
Most of the companies in India for turnover less than 5 cr per annum offer around 24% per annum return
Q:
“Margins for premium cosmetics (skin care) in China through the complete supply chain” => CHINA “or” World-Wide (it’s all the Same!)
=> Assuming, Suggested Retail Price is : $50
(1.7oz/50gm “Glass Air-Less Pump” Packaging, with an Outer Paper Box)
A:
1) Retailer (Sephora etc…): 50% : Minimum
– Extremely “Saturated” Scenario
– Too many Large Brands (Multi-Billion Dollar Big 10) in this space offering the same deal [5-10 Brands “own” 98% of this Space/SKU’s on Shelf]
-> IF the Brand proves to be a Success (by achieving Projected Revenue);
Then this may drop down to : 40% (Lowest Possible).
2) Distributor : 30% : Minimum + A Monthly Retainer (until Brand is a success); Will drop down to 25% (lowest) after the initial Launch Period.
-> Fyi: It’s not your headache to “Calculate” for anyone else besides, Master Distributor (Importer)
3) Manufacturer : 20% (FOB Terms – to the Distributor)
– Private Label “or” In-House Manufacturing ?
– IF You’re an Entrepreneur, approaching a Private Label Manufacturer,
Then you are not going to get more than : 5% to 8% (NET).
My 2 Cents (Advice!) for getting into this Space:
– Please DO NOT even think about entering this Space IF:
a) You are not a Celebrity
(International Star, with Millions of Followers on Various Social Media Platforms) -> Of Course, you can always partner with one.
“But” almost every Licensing Firm, will always be there in front of you:)
b) You don’t – own your own Factory (with Scale Up Capabilities).
c) You are not a *Cosmetic Chemist (who has *Finally discovered “the Fountain of Youth”)
d) You don’t have access to a *Start-Up FUND in the range of
$10 to $20 Million (if you’re a *Harvard “Entrepreneur”:-)
—–
IF you’re already “an Industry Insider” ; Then all the above does not apply:)
What is Profit Margin in Excel, here’s the simple step?
Struggling with profit and loss? Or still, figuring out how to calculate the profit margin in excel? Here is your answer, the Profit margin is an important figure for business because it tells the percentage of each profited sale. Profit margins are important when pricing products, pursuing financing and generating sales reports.
If you create the spreadsheet and input the formula properly, Microsoft Excel will calculate profit margins. If you need to calculate a profit margin, you can easily do so with a simple formula that uses the sale price and the cost. Knowing how to calculate your profit margin will help you take control of your business and ensure that each sale nets the profit you expect.
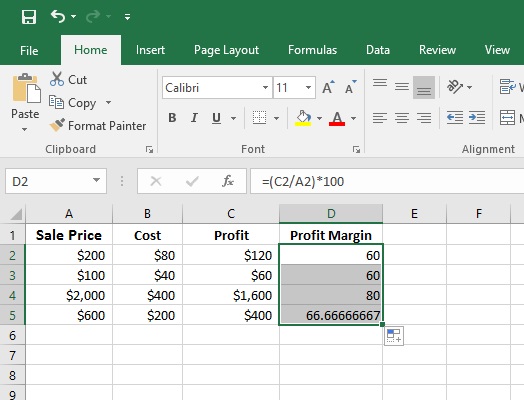
Calculate the profit Margin in column D using this formula in cell D2:
=(C2/A2)*100 This formula will calculate the percentage value of Profit margin. Now, Press ENTER. Do the same for another cell of column D. You will get all profit margin for each Sale.
Calculating Sale price from cost and Margin
on original cost 24.9 and margin 85%.
Sell Price = Cost / (1- Margin %).
In your example, 24.9/(1-.85) will give you a selling price of 166.
Here is the excel function: =A2/(1-B2) where A2=cost and B2=margin% (in decimal form)
How to Calculate Profit Margin in Excel Profit Margin Formula
Check the picture.

Step 4: Now we will calculate the profit Margin in column D using this formula in cell D2:
=(C2/A2)*100 This formula will calculate the percentage value of Profit margin. Now, Press ENTER. Do the same for another cell of column D. You will get all profit margin for each Sale.
How to calculate profit margin
- Find out your COGS (cost of goods sold). For example
$30. - Find out your revenue (how much you sell these goods for, for example
$50). - Calculate the gross profit by subtracting the cost from the revenue.
$50 - $30 = $20 - Divide gross profit by revenue:
$20 / $50 = 0.4. - Express it as percentages:
0.4 * 100 = 40%. - This is how you calculate profit margin… or simply use our gross margin calculator!
As you can see, margin is a simple percentage calculation, but, as opposed to markup, it’s based on revenue, not on Cost of Goods Sold (COGS).
Gross margin formula
The formula for gross margin percentage is as follows: gross_margin = 100 * profit / revenue (when expressed as a percentage). The profit equation is: profit = revenue - costs, so an alternative margin formula is: margin = 100 * (revenue - costs) / revenue.
Now that you know how to calculate profit margin, here’s the formula for revenue: revenue = 100 * profit / margin.
And finally, to calculate how much you can pay for an item, given your margin and revenue (or profit), do: costs = revenue - margin * revenue / 100
A note on terminology
All the terms (margin, profit margin, gross margin, gross profit margin) are a bit blurry and everyone uses them in slightly different contexts. For example, costs may or may not include expenses other than COGS – usually, they don’t. In this calculator, we are using these terms interchangeably and forgive us if they’re not in line with some definitions. To us, what’s more important is what these terms mean to most people, and for this simple calculation the differences don’t really matter. Luckily, it’s likely that you already know what you need and how to treat this data. This tool will work as gross margin calculator or a profit margin calculator.
So the difference is completely irrelevant for the purpose of our calculations – it doesn’t matter in this case if costs include marketing or transport. Most of the time people come here from Google after having searched for different keywords. In addition to those mentioned before, they searched for profit calculator, profit margin formula, how to calculate profit, gross profit calculator (or just gp calculator) and even sales margin formula.
Margin vs markup
The difference between gross margin and markup is small but important. The former is the ratio of profit to the sale price and the latter is the ratio of profit to the purchase price (Cost of Goods Sold). In layman’s terms, profit is also known as either markup or margin when we’re dealing with raw numbers, not percentages. It’s interesting how some people prefer to calculate the markup, while others think in terms of gross margin. It seems to us that markup is more intuitive, but judging by the number of people who search for markup calculator and margin calculator, the latter is a few times more popular.
FAQ
What’s the difference between gross and net profit margin?
Gross profit margin is your profit divided by revenue (the raw amount of money made). Net profit margin is profit minus the price of all other expenses (rent, wages, taxes etc) divided by revenue. Think of it as the money that ends up in your pocket. While gross profit margin is a useful measure, investors are more likely to look at your net profit margin, as it shows whether operating costs are being covered.
Can profit margin be too high?
While a common sense approach to economics would be to maximise revenue, it should not be spent idly – reinvest most of this money to promote growth. Pocket as little as possible, or your business will suffer in the long term! There are also certain practices that, despite short term profit, will cost you more money in the long run, e.g., importing resources from a country likely to be subject to economic sanctions in the future, or buying a property that will be underwater in 5 years.
What is margin in sales?
Your sales margin is the product of the selling price an item or service, minus the expenses it took to get the product to be sold, expressed as a percentage. These expenses include: discounts, material and manufacturing costs, employee salaries, rent, etc. While this is very similar to net profit, sales margin is in per unit terms.
How do I calculate a 20% profit margin?
- Express 20% in its decimal form, 0.2.
- Subtract 0.2 from 1 to get 0.8.
- Divide the original price of your good by 0.8.
- There you go, this new number is how much you should charge for a 20% profit margin.
What is a good margin?
There is no definite answer to “what is a good margin” – the answer you will get will vary depending on whom you ask, and your type of business. Firstly, you should never have a negative gross or net profit margin, otherwise you are losing money. Generally, a 5% net margin is poor, 10% is okay, while 20% is considered a good margin. There is no set good margin for a new business, so check your respective industry for an idea of representative margins, but be prepared for your margin to be lower. For small businesses, employees are often your main expense.
How do I calculate margin in Excel?
While it’s easier to use the Omni Margin Calculator, it is useful to know how to calculate margin in Excel:
- Input the cost of goods sold (for example, into cell A1).
- Input your revenue on the product (for example, into cell B1).
- Calculate profit by subtracting cost from revenue (In C1, input =B1-A1) and label it “profit”.
- Divide profit by revenue and multiply it by 100 (In D1, input =(C1/B1)*100) and label it “margin”.
- Right click on the final cell and select Format Cells.
- In the Format Cells box, under Number, select Percentage and specify your desired number of decimal places.
How do I calculate a 10% margin?
- Make 10% a decimal by dividing 10 by 100 to get 0.1.
- Take 0.1 away from 1, equalling 0.9.
- Divide how much your item cost you by 0.9.
- Use this new number as your sale price if you want a 10% profit margin.
Are margin and profit the same?
Although both measure the performance of a business, margin and profit are not the same. All margin metrics are given in percent values, and therefore deal with relative change, good for comparing things that are operating on a completely different scale. Profit is explicitly in currency terms, and so provides a more absolute context – good for comparing day to day operations.
How do I calculate a 30% margin?
- Turn 30% into a decimal by dividing 30 by 100, which is 0.3.
- Minus 0.3 from 1 to get 0.7.
- Divide the price the good cost you by 0.7.
- The number that you receive is how much you need to sell the item for to get a 30% profit margin.
More on How to calculate markup from margin?
- Turn your margin into a decimal by dividing the percentage by 100.
- Subtract this decimal from 1.
- Divide 1 by the product of the subtraction.
- Subtract 1 from product of the previous step.
- You now have markup expressed in decimal form!
- If you want to have markup in percentage form, multiply the decimal by 100.
The formula for calculating the margin in Excel
Create a table in Excel, as it shown in the picture:
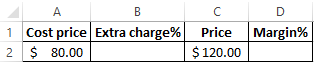
In the cell under the word margin D2 enter the following formula:
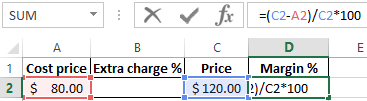
As a result, we obtain an indicator of the dimension of the margin, we had 33.3%.
How to calculate the margin in percentage if we know the extra charge?
For obviousness, we give a practical example. After collecting the reporting data, the firm received the following indicators:
- Volume of sales = 1000$
- Extra charge = 60%
- Based on the obtained data we calculate the prime cost (1000 – x) / x = 60%
Hence we have x = 1000 / (1 + 60%) = 625
We calculate the margin:
- 1000 – 625 = 375
- 375/1000 * 100 = 37.5%
From this example follows the algorithm of the formula for counting for Excel:
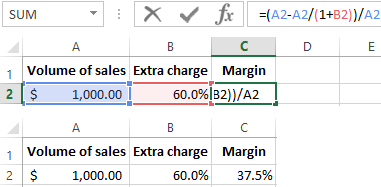
How to calculate the extra charge in percentage if you know the margin?
Reports on sales for the previous period brought the following indicators:
- Sales volume = 1000$
- Margin = 37.5%
- Based on the obtained data we calculate the prime cost (1000 – х) / 1000 = 37,5%
Hence we have x = 625
We calculate the extra charge:
- 1000 – 625 = 375
- 375/625 * 100 = 60%
Example of an algorithm for calculating for Excel:
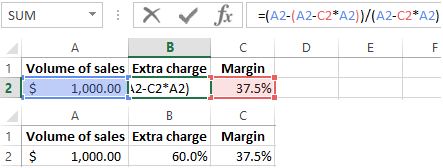
Gross Income = margin on invoice + support \incentive earned from company.
Expenses= warehouse rentals+ manpower dedicated + vehicle running cost+ others
investment= (stocks from company + credit in market + investment in offices assets + vehicle down payment) -co credit.
Most of the companies in India for turnover less than 5 cr per annum offer around 24% per annum return
the manpower calculation in FMCG is 40 outlet cover by one sales man in the day. one week covered outlets are 40*6=240 and if you want weekly coverage in the market then on every 240 outlets need one sales man.
fortnightly coverage= 12 days*40=480 outlet and repeat in the next 15 days so coverage of 480 outlets in the month by one sales man.
so if the town has 500 outlets then 1 sales man is enough for fortnightly coverage and if weekly coverage then 2 sales man required.
The return on investment calculation is simple as expained below.
ROI = ( Revenue – Expenses)/Investment
Net Income = Revenue – Expenses.
Revenue : Its a fix margin which is given on the total purchase for the month. For e.g. is the distributor margin is 5% then on purchase of 1 CR it will be 5 lacs for the month.
Expenses : It includes the expenses occurred for the business on monthly basis.
- Salary of sales man, vehicle driver, vehicle helper, loaders, computer operator, go down staff.
- Vehicle operating cost monthly (if its owned vehicle then fuel cost will be part of of expenses, cost of the depreciated cost of vehicle will be part of investment, if its market hired vehicle then fuel & hiring cost will be part of expenses).
- Godown rent, electricity bill, stationery expenses, telephone bill, internet charges, any other administration expenses.
- Any interest on borrowed capital will be part of expenses but such capital will not be part of investment, any cash discount being given to wholesalers.
Investment : This typically includes the stock maintained in number of days( for e.g. stock holding is equal to 7 days of sales), credit given in market in number of days ( for e.g. 15 days credit, it means that credit is equal to 15 days worth of sales in the month), investment in claims which has to be reimbursed by the company ( it will be typically 5% of the monthly revenue).
Now for e.g. if the net income is 2 lacs on a monthly business of 100 lacs (1 cr) then the monthly ROI is 2%, which will translate into annual ROI if 24%. ( Annual ROI is 12* monthly net income/Investment). The investment will remain fix each month so its a fix cost which will not change. Generally a good distributor who is hardworking, fully involved in business will make 2% monthly.
Anything above 20% is very healthy ROI keeping in mind the kind of returns you get from bank on FD will not be more than 8%.
Formula for R.O.I
Return on Investment
Gross Profit – Expenses = Net Profit
=
Net Profit / Investment × 100%
Poor R.O.I = Less than 24%
Medium R.O.I = 24%
Healthy R.O.I = Above 24-36%
Things To be considered in
Investment
Paid-up-stocks
Closing Stocks
Claims
Credit in market
Damages
Goods in transit
Balance amount with companies
Expenses
Office Expenses
Salary to Staff salesman-delivery man & helper
Electric-Telephone-Internet Cost
Stationery
Maintenance & Vehicle Depreciation
Bank charges
Cash discounts
Godown Rent
Misc…. Exp

Trade Schemes in Sales (FMCG/FMCD/Telecom)
Retailers have two ways of earning profit from selling a product from a brand:
1. The Margin on products (Selling Price – Buying Price)
2. Trade Marketing Schemes
Trade marketing are incentives for shopkeepers to pursue them to promote the brand to the end customers. As shopkeepers (especially in tier 3, 4cities) are often opinion influencers.

Trade fairs, conclaves, and fests.


These schemes promote higher purchases from the retailers by giving strategic discounts such as Quantity discounts, Value discounts, Extra product schemes, etc.
Quantity Scheme: It is a type of secondary scheme which is divided into various windows of discounts with respect to the quantity sold.

E.g.
50 Piece – 1%
200 Piece – 2%
500 Piece – 3%
Value Scheme: It is like a Quantity scheme but is pegged to a certain monetary value.

E.g.
Rs. 5000 – 1%
Rs. 20000 – 2%
Rs. 100000 – 3%

Extra product scheme: It is a secondary scheme where retailers get one or more extra products on buying a particular quantity.
E.g.
Buy 11 Piece – Get 1 Piece Free
Buy 9 Piece – Get 1 Piece Free
3. Loyalty Program:
Companies desire long-term engagement with retailers and to ensure that, they use loyalty programs.
Usually, companies have Quarterly, Half-yearly, and Yearly programs with retailers. These programs have certain conditions for qualification such as the value of purchase, range of purchase, expected activity, etc.
Conditions vary from industry to industry. Long-term programs provide rewards such as Vacation trips and credit notes.
It also helps in decrease undercutting hence maintaining a healthy market operating price of the product.
FMCG SCHEME CALCULATOR
1+1 = 50.00%
2+1 = 33.33%
3+1 = 25.00%
4+1 = 20.00%
5+1 = 16.66%
6+1 = 14.29%
7+1 = 12.50%
8+1 = 11.11%
9+1 = 10.00%
10+1 = 9.09%

11+1 = 8.33%
12+1 = 7.69%
13+1 = 7.14%
14+1 = 6.66%
15+1 = 6.25%
16+1 = 5.89%
17+1 = 5.55%
18+1 = 5.26%
19+1 = 5.00%
20+1 = 4.76%
Example: -If the scheme is 11 + 1, then it will be calculated as
11+1 = 12 Therefore 1÷12 ×100 = 8.33%
Formula of Mark-Up and Mark-Down
Mark down is usually flat discounts like schemes
Example 10 % Discount On M.R.P
M.R.P is 100 Rs
Then
10-10% = 90
Price to Retailer is Rs 90/- & Margin given by a Sales Officer is 10 %
Then Calculation will be
10/90 x 100 = 1.11%
Therefore 90 x 1.11% = 100 —> M.R.P
11.11% for both the cases
90 X 1.11111 = 100 Mark up
or
100 ÷ 1.11111 = 90 Mark down
Retail Margin 10%
Price = 10/1.10 = 9.09
For Mark down:
Discount 10%
Price = 10-10%= 9
If the mrp of a product is 25 and price to retailer is 20 Rupees what is the margin?
(25-20%=20) = 20%
*FMCG Scheme calculator* :
1+1 = 50.00%
2+1 = 33.33%
3+1 = 25.00%
4+1 = 20.00%
5+1 = 16.66%
If the scheme is 11 + 1 then it will be calculated as 1÷12 % = 8.33%
What is the 87.5% scheme in FMCG?





Retailers say that margins from FMCG (fast moving consumer goods) companies have gone up from 14-15 per cent to 17-19 per cent as they jostle for shelf space with retailers’ private labels. “Earlier, FMCG companies were servicing us through distributors and the terms of the trade were not favouring modern trade.
What is a good profit margin for small business?
An NYU report on U.S. margins revealed the average net profit margin is 7.71% across different industries. But that doesn’t mean your ideal profit margin will align with this number. As a rule of thumb, 5% is a low margin, 10% is a healthy margin, and 20% is a high margin.
How do you calculate profit margin for retail?
To calculate the retail margin percent, divide the retail margin by the selling price and multiply by 100. For example, if you have a retail margin of $10 on an item that you sell for $50, the retail margin percent equals 20 percent.
How is retail P&L calculated?
P&L STATEMENT COMPONENTS
How is MRP margin calculated?
Which products are in demand?
Products that are most in demand and selling online in India
How big is the FMCG industry in India?
The Indian FMCG sector is the fourth largest in the Indian economy and has a market size of $13.1 billion. This industry primarily includes the production, distribution and marketing of consumer packaged goods, that is those categories of products which are consumed at regular intervals.
What is the profit margin in retail shop in India?
Profit in different retail sector . GROCERY : 20% . it can varies upto 30 %. For biscuit it is 10% and chocolate it is 10%. if MRP of biscuit is 10 rupees Retailer get 1 rupee .EDIBLE OIL is highly profit area . Super market in city area get high profit in edible oil. retailer get above 30% profit edible oil area
How is price calculated in FMCG trade scheme?
Assuming MRP of 1 unit of X is Rs 150/-. 1 Case of X comprises of 24 units of X and hence 1 case of X is valued at Rs 3600/- (at MRP). The company decides to roll-out a primary scheme of 4% and runs a Secondary Scheme in the form of QPS. The QPS is designed for whole-sale and high volume retail outlets and is as follows: